01. Python Datatypes & Operators
1. Code Style
PEP8, The style guide provided by Python
2. Variables
The name of data
- Developers can handle data without memorizing memory addresses.
- Developers can intuitively understand the meaning of the data.
2.1. Naming Rules
- a combination of English, numbers, and '_'
- can't start with numbers
- can't use keywords or reserved words
2.2. Type Hint (after python 3.5)
- Ex.
count_point: int = 10
3. Non-Container Data Types
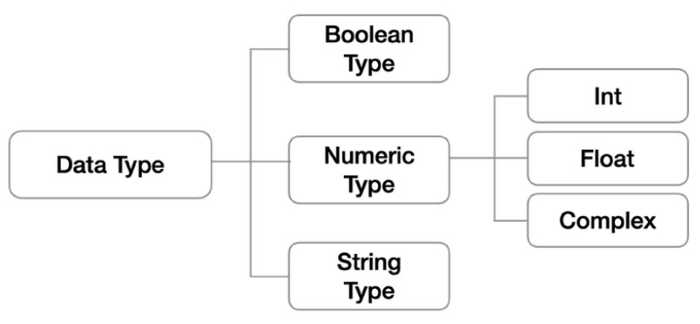
3.1. Boolean Type
- Basics
TrueFalsebool(data)
ReturnTrueorFalsebased on the datanot data
The opposite of the boolean result of the data
- Characteristics
- immutable
- non-iterable
- Falsy value
0, 0.0, (), [], {}, '', None
- Typecasting
int(True) == 1int(false) == 0
3.2. Numeric Type
-
Characteristics
- immutable
- non-iterable
-
integer
- Decimal numbers are the default expression
- binary:
42 == 0b101010 - Octal:
42 = 0o52 - Hexa:
42 == 0x2a
- binary:
- Typecasting
int('3') == 3 int('3.5') == error int(3.5) == 3
- Decimal numbers are the default expression
-
float
- Expressions
- 3.14
- 314e-2
-
Floating point error
# use round() round(3.141592, 2) == 3.14 # use sys.float_info.epsilon import sys abs(a - b) <= sys.float_info.epsilon # use math.isclose import math math.isclose(a, b) -
Typecasting
float('3.5') == 3.5 int('3') == 3.0 int(3) == 3.0
- Expressions
3.3. String Type
- Basics
- Expressed with '' or ""
- multiple lines string data is expressed with triple quotes
- Characteristics
- immutable
- error:
(a = 'hello'); a[0]='b'
- error:
- Iterable
for char in a:
- immutable
- Escape sequences
reserved key meaning \n Enter \t tab \r carriage return \0 Null \\ | \' ' \" " \n Enter - Typecasting
s = 'string' print(list(s)) # ['s', 't', 'r', 'i', 'n', 'g'] print(tuple(s)) # ('s', 't', 'r', 'i', 'n', 'g') print(dict(s)) # error print(set(s)) # {'r', 'i', 'n', 's', 'g', 't'} - Methods
Method description output change(immuatble) .upper() change to upper letter str X .lower() change to upper letter str X .swapcase() swap upper->lower, lower->upper str X .title() change the first letter to upper str X .count('s', start, end) count 's' between srint[start:end] int X .find('s', start, end) find index of 's' from the leftreturn -1 when doesn't exist int X .rfind('s', start, end) find index of 's' from the rightreturn -1 when doesn't exist int X .index('s', start, end) find index of 's' from the lefterror when doesn't exist int X .rindex('s', start, end) find index of 's' from the righterror when doesn't exist int X .startswith('s', start, end) whether the string starts with Bool X .endsswith('s', start, end) whether the string endss with Bool X .strip() remove space bf/af of the string str X .strip('s') remove the chr bf/af of the string str X .rstrip() remove space af of the string str X .lstrip() remove space bf of the string str X .replace('s1','s2',[count]) replace 's1' to 's2' in the str object [count]times str X .split('s') divide string by 's' list X .splitlines() divide string by line list X .join(iterbale) combine iterbale object with string str X .center(i, 'c') center aligned with i-width filled with 'c' str X .ljust(i, 'c') left aligned with i-width filled with 'c' str X .rjust(i, 'c') right aligned with i-width filled with 'c' str X .zfill(i) right aligned with i-width filled with '0' str X
3.4. None
- Basic
- Means that there is no value
- use
isinstead of==when compared to other data
4. Container Data Types
Can contain multiple different data types
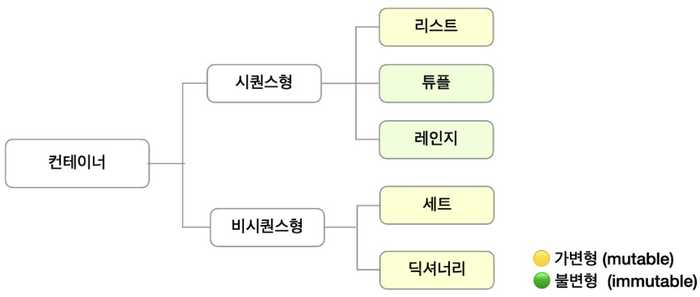
- Sequence
data is ordered == can use index - Non-Sequence
data isn't ordered == can't use index
4.1. List Type
-
Basics
- produce
my_list = [] another_list = list()
- produce
-
Characteristics
- Ordered
my_list[0]
- Mutable
my_list = [1, 2, 3]; list1[0]='a'
- Iterable
for _ in my_list:
- Ordered
-
Typecasting
l = [1, 2, 3, 4] print(str(l)) # [1, 2, 3, 4] print(tuple(l)) # (1, 2, 3, 4) print(dict(l)) # error print(set(l)) # {1, 2, 3, 4} -
Operators
[2, 3] + [4, 5, 6] == [2, 3, 4, 5, 60] ['Python'] * 3 == ['Python', 'Python', 'Python'] -
Methods
Method description output change .append(object) add object None O .extend(iterbale) add elements of an iterableitems in the outmost iterbale obj None O .clear() clear the list None O .copy() return the shallow copy list X .count() number of elements int X .index(obj, start, end) find index of 's' from the lefterror when doesn't exist int X .insert(i, obj) insert obj in l[i]; if [i]is bigger than length >> insert at the last None O .pop(i) pop l[i] obj O .remove(obj) remove obj in l None O .reverse() reverse the list None O .sort(reverse=False) sor the list None O
4.2. Tuple Type
- Basics
my_tuple = () my_tuple_2 = 1, # (1,) my_tuple_3 = 'hello', # ('hello',) my_tuple_3 = 1, 2, 3 # (1, 2, 3) another_list = tuple() - Characteristics
- Ordered
my_tuple[0]
- Immutable
my_tuple = (1, 2, 3); my_tuple[0]='a'; # error-
day_name = ('월', '화', '수') day_name += True, False >>> ('월', '화', '수', True, False) # original day_name is deleted
- Iterable
for _ in my_tuple:
- Ordered
- Typecasting
t = (1, 2, 3, 4) print(str(t)) # (1, 2, 3, 4 print(list(t)) # [1, 2, 3, 4] print(dict(t)) # error print(set(t)) # {1, 2, 3, 4} - Operators
(2, 3) + (4, 5, 6) = (2, 3, 4, 5, 60) ('Python') * 3 = ('Python', 'Python', 'Python') - Methods
Method description output change .count() number of elements int X .index(obj, start, end) find index of 's' from the lefterror when doesn't exist int X
4.3. Range Type
- Basics
range(n) # 0 ~ (n-1) : +1 range(n, m) # n ~ (m-1) : +1 range(n, m, s) # n ~ (m-1) : +s - Characteristics
- Ordered
my_range[0]
- Immutable
my_range = range(3); my_range[0]='a'; # error
- Iterable
for _ in range(5):
- Ordered
- Typecasting
r = (1, 5) print(str(t)) # (1, 2, 3, 4) print(list(t)) # [1, 2, 3, 4] print(tuple(t)) # (1, 2, 3, 4) print(dict(t)) # error print(set(t)) # {1, 2, 3, 4}
4.4. Dictionary Type
-
Basics
- key: immutable data
- value: any data
my_dict = {} another_list = dict() -
Characteristics
- Mutable
my_dict = {'Jerry':45}; my_dict['Jerry']='a';
- Iterable
for _ in my_dict:
- Mutable
-
Typecasting
d = {'name': 'ssafy', 'year': 2020} print(str(d)) # {'name': 'ssafy', 'year': 2020} print(list(d)) # ['name', 'year'] print(tuple(d)) # ('name', 'year') print(set(d)) # {'name', 'year'} -
Methods
Method description output change .clear() clear the dict None O .copy() return the shallow copy dict X dict.fromkeys(iterable, value) make dict that has itms of iterable as key dict X .get(key,[default=None]) get value of key;if there is no key return [default] obj X .items() return [(key, items)] dict_items X .keys() return [keys,] dict_keys X .values() return [items,] dict_values X .pop(key) pop dict(key) obj O .popitem() pop the last inserted (key,value) tuple O .setdefault({key:value}) if alreayd exist return original dict(key) obj or None X .update() update dict None O - update()
- if key is a string
x.update(a=900, f=60) - if key is a number
x.update({1:900, 2:800})
- if key is a string
- update()
4.5. Set Type
- Basics
{1, 2, 3} set() # print: set() - Characteristics
- Mutable
my_set.pop()
- Iterable
for _ in my_set:
- Mutable
- Typecasting
s = {1, 2, 3, 4} print(str(d)) # {1, 2, 3, 4} print(list(d)) # [1, 2, 3, 4] print(tuple(d)) # (1, 2, 3, 4) print(dict(d)) # error - Methods
B is an iterable object(set, tuple, list ...)Method description output change .add(obj) add obj None O .clear() clear the set None O .copy() return shallow copy None O A.difference(B) return A - Bset X A.difference_update(B) A = A - BNone O .discard(obj) remove objNo error even if there is no obj None O A.intersection(B) return A & Bset X .intersection_update() A = A & BNone O A.isdisjoint(B) A & B == Nonebool X A.issubset(B) A & B == Bbool X A.issuperset(B) A & B == Abool X .pop() pop ==arbitary== obj O .remove() remove objerror when there is no obj None O A.symmetric_differnece(B) return A ^ Bset X A.symmetric_differnece_update(B) A = A ^ BNone O A.union(B) return A + Bset X A.update(B) A = A + BNone O
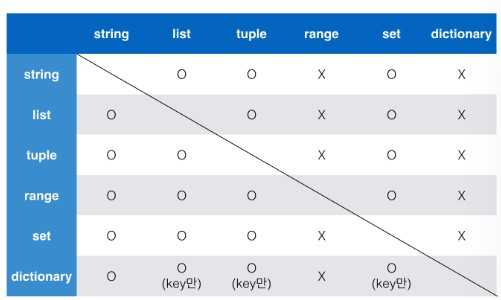
4.5. Typecasting table
4.6. Copy Mutable Data
The mutable data type has several methods of copying.
It's divided into three stages according to the degree of connection between the copied data and the original data.
A is an mutable data
-
Not Copied
B = A # Not copied B is A == True -
Shallow Copy
The elements which depth are more than one are not copiedimport copy B = copy.copy(A) # In the case of list B = A[:] -
Deep Copy
All the elements are copied regardless of their depthimport copy B = copy.deepcopy(A)
5. Operators
5.1. Priority of operators
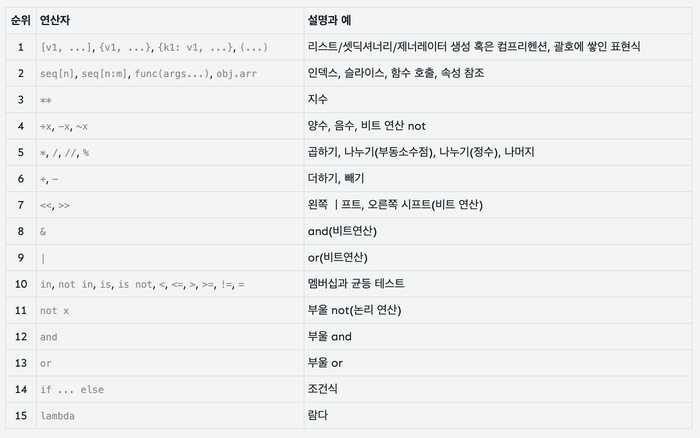
5.2. Arithmetic Operators
| arithmetic operator | meaning |
|---|---|
| + | plus |
| - | minus |
| * | multiplication |
| / | division |
| // | quotient |
| % | remainder |
| ** | square |
5.3. Comparison Operators
| comparision operator | meaning |
|---|---|
| < | under |
| <= | or less |
| > | above |
| >= | or more |
| == | same(value) |
| != | different(value) |
| is | same(object) |
| is not | different(object) |
5.4. Logician Operators
| logician operator | meaning |
|---|---|
| and | both True? |
| or | either True? |
| not | toggle the bool |
5.4.1. Short Circuit Evaluation
returns the value that confirm the result of the logical operation
'a' and 'b' # 'b'
'a' or 'b' # 'a'
'a' and 'b' in 'aeiou' # False
'b' and 'a' in 'aeiou' # True
5.5. Membership Operators
check whether the data is in an iterable data
| membership operator | meaning |
|---|---|
| in | is in ? |
| not in | isn't in ? |
5.6. Bit Operators
| bit operator | meaning |
|---|---|
| & | bit and |
| | | bit or |
| ^ | bit xor |
| ~ | bit not |
| << | move bit left == *2 |
| >> | move bit right == //2 |
다음 포스트