03. JavaScript Async
1. Synchronous and Asynchronous
Synchronous
- Process in order
- Wait for the response to a request.
Asynchronous
- Process in parallel
- Don't Wait for the response -> Better user experience
1.1. Asynchronous JavaScript
JavaScript is a single-thread language, but it still can handle things asynchronously.
function slowRequest(callBack) {
console.log('1. A long time process started')
setTimeout(function () {
callBack()
}, 3000)
}
function myCallBack() {
console.log('2. The long time process ended')
}
slowRequest(myCallBack)
console.log('3. Another short process')
// 1. A long time process started
// 3. Another short process
// 2. The long time process ended
1.2. JavaScript Runtime
The environment that helps JavaScript being asynchronous
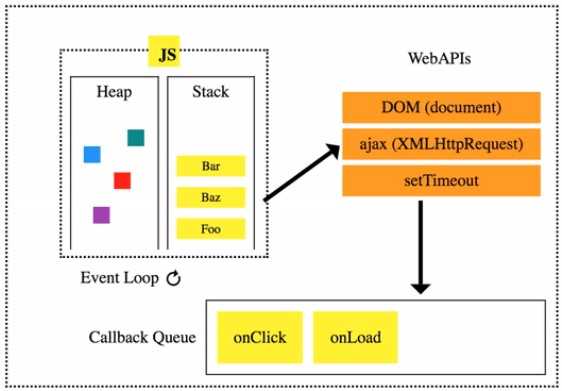
- All tasks are processed after entering the Call Stack.
- If a long-lasting task enters the stack, it's sent to the Web API and processed separately.
- Tasks that have been processed in Web API are sequentially entered into the Task Queue.
- When the Event Loop detects that the stack is empty, it sends the oldest task in the queue to the stack.
2. Axios
The library for asynchrnous HTTP communciation. It can be installed with npm in node.js, and can be used with CDN in browser.
2.1. The Structure of Axios
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<script>
axios.get('URL')
.then(callback in case of success)
.catch(callback in case of failure)
<button>Cat</button></button>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<script>
const catImageSearchURL = 'https://api.thecatapi.com/v1/images/search'
const btn = document.querySelector('button')
btn.addEventListener('click', function () {
// axios.get(catImageSearchURL)
axios({
method: 'get',
url: catImageSearchURL
})
.then((response) => {
imgElem = document.createElement('img')
imgElem.setAttribute('src', response.data[0].url)
document.body.appendChild(imgElem)
})
.catch((error) => {
console.log('Fail!')
})
console.log('Success!')
})
// Success!
// response object
// axios library works asynchronously
</script>
2.2. Promise
Promise is the object for giving order to asynchronous process. (chaining)
- methods
then(onFulfilled)- Runs the
onFulfilledfunction if the Promise is fulfilled onFulfilledhas one parameter, the fulfillment value.- Returns a promise object
- Runs the
catch(onReject)- Runs the
onRejectfunction if the Promise is rejected onRejectfunction has one parameter: the rejection reason.- Returns a promise object
- Runs the
work1()
.then((result1) => {
// work 2
return result2
})
.then((result2) => {
// work 3
return result3
})
.catch((error) => {
// error handling
})
2.2. Promise and Await
Promise & Await를 활용한 4가지 비동기 함수 처리방법.md
3. AJAX
3.1. AJAX
AJAX stands for Asynchronous JavaScript And XML. In a nutshell, it is the use of the XMLHttpRequest object to communicate with servers. It can send and receive information in various formats, including JSON, XML, HTML, and text files.
3.2. data-* attribute
data-*attribute make data can be exchanged between HTML and DOM.
<div data-my-id="my-data"></div>
<script>
const myId = event.target.dataset.myId
</script>
3.3. Example with Django
csrf-token is in the hidden input tag which name is "csrfmiddlewaretoken"
3.3.1. Follow
<div>
팔로워 : <span id="followers-count">{{ person.followers.all|length }}</span> /
팔로잉 : <span id="followings-count">{{ person.followings.all|length }}</span>
</div>
<div>
<form id="follow-form" data-user-id="{{ person.pk }}">
{% csrf_token %} {% if request.user in person.followers.all %}
<input type="submit" value="언팔로우" />
{% else %}
<input type="submit" value="팔로우" />
{% endif %}
</form>
<div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<script>
const form = document.querySelector('#follow-form')
const csrftoken = document.querySelector(
'[name=csrfmiddlewaretoken]'
).value
form.addEventListener('submit', function (event) {
event.preventDefault()
const userId = event.target.dataset.userId
axios({
method: 'post',
url: `/accounts/${userId}/follow/`,
headers: { 'X-CSRFToken': csrftoken },
})
.then((response) => {
const isFollowed = response.data.is_followed
const followBtn = document.querySelector(
'#follow-form > input[type=submit]'
)
if (isFollowed === true) {
followBtn.value = '언팔로우'
} else {
followBtn.value = '팔로우'
}
// 팔로우, 팔로워 인원 수
const followersCountTag = document.querySelector('#followers-count')
const followingsCountTag =
document.querySelector('#followings-count')
const followersCount = response.data.followers_count
const followingsCount = response.data.followings_count
followersCountTag.innerText = followersCount
followingsCountTag.innerText = followingsCount
})
.catch((error) => {
console.log(error.response)
})
})
</script>
</div>
</div>
@require_POST
def follow(request, user_pk):
if request.user.is_authenticated:
User = get_user_model()
me = request.user
you = User.objects.get(pk=user_pk)
if me != you:
if you.followers.filter(pk=me.pk).exists():
you.followers.remove(me)
is_followed = False
else:
you.followers.add(me)
is_followed = True
context = {
'is_followed': is_followed,
'followers_count': you.followers.count(),
'followings_count': you.followings.count(),
}
return JsonResponse(context)
return redirect('accounts:profile', you.username)
return redirect('accounts:login')
3.3.2. Like
{% for article in articles %}
<p>
<b
>작성자 :
<a href="{% url 'accounts:profile' article.user %}"
>{{ article.user }}</a
></b
>
</p>
<p>글 번호 : {{ article.pk }}</p>
<p>제목 : {{ article.title }}</p>
<p>내용 : {{ article.content }}</p>
<div>
<form class="like-forms" data-article-id="{{ article.pk }}">
{% csrf_token %} {% if request.user in article.like_users.all %}
<input type="submit" value="좋아요 취소" id="like-{{ article.pk }}" />
{% else %}
<input type="submit" value="좋아요" id="like-{{ article.pk }}" />
{% endif %}
</form>
</div>
<a href="{% url 'articles:detail' article.pk %}">상세 페이지</a>
<hr />
{% endfor %}
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<script>
const forms = document.querySelectorAll('.like-forms')
const csrftoken = document.querySelector(
'input[name=csrfmiddlewaretoken]'
).value
forms.forEach((form) => {
form.addEventListener('submit', function (event) {
event.preventDefault()
const articleId = event.target.dataset.articleId
axios({
method: 'post',
url: `http://127.0.0.1:8000/articles/${articleId}/likes/`,
headers: { 'X-CSRFToken': csrftoken },
})
.then((response) => {
const isLiked = response.data.is_liked
const likeBtn = document.querySelector(`#like-${articleId}`)
if (isLiked === true) {
likeBtn.value = '좋아요 취소'
} else {
likeBtn.value = '좋아요'
}
})
.catch((error) => {
console.log(error.response)
})
})
})
</script>
@require_POST
def likes(request, article_pk):
if request.user.is_authenticated:
article = Article.objects.get(pk=article_pk)
if article.like_users.filter(pk=request.user.pk).exists():
article.like_users.remove(request.user)
is_liked = False
else:
article.like_users.add(request.user)
is_liked = True
context = {
'is_liked': is_liked,
}
return JsonResponse(context)
return redirect('accounts:login')