01. Java Basics
- 1. Program and OS
- 2. Data representation
- 3. JVM(Java Virual Machine)
- 4. Hello SSAFY
- 5. Java IDE Intro
- 6. Variable and Data type
- 7. Operator
- 8. Control flow - condition
- 9. Control flow - loop
- 10. Array
- 11. Multidimensional Array
1. Program and OS
1.1. Program
- the collection of commands to perfrom sepcific task
1.2. Operating System
- Software that manage computer hardware and provide service and platform for application SW
2. Data representation
- Binary data
- 1Byte as numerical value(==the first one is sign bit==)
- -128 ~ 127
3. JVM(Java Virual Machine)
- Subjects executing Java Byte code
- Java Byte Code
- the middle file(.class) between source code and binary code
- Makes Java Byte code be able to excuted on every OS
4. Hello SSAFY
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("Hello SSAFY")
}
}
- javac Hello.java
- Hello.java -> Hello.class
- java Hello
- excuting Hello.class
- eclipse
- IDE(Integrated Developmend Environment)
- Support programming including upper procedures
5. Java IDE Intro
<package> // folder
<library>
<src> // source code folder
<.java> //make class in the package.src
<bin> // java byte code folder
<.clss>
5-1. main method
- where the code starts!!
- fixed form
public static void main(String[] args){}
5-2. comment
- line comment:
// - range comment:
/* */ - documentation comment:
/** */- explanation for the function
5-3. Print
System.out.
-
print: print -
println: print and change the line -
printfpublic static void main(String[] args) { System.out.printf("%d \n", 10); // 10 System.out.printf("%o \n", 10); // 12 System.out.printf("%x \n", 10); // a System.out.printf("%X \n", 10); // A System.out.printf("%4d \n", 10); // 10 System.out.printf("%-4d \n", 10); //10 System.out.printf("%04d \n", 10); //0010 System.out.printf("%f \n", 10.1); //10.100000 System.out.printf("%.2f \n", 10.1); //10.10 System.out.printf("%s \n", "Kim"); //Kim System.out.printf("%c \n", "O"); //O }
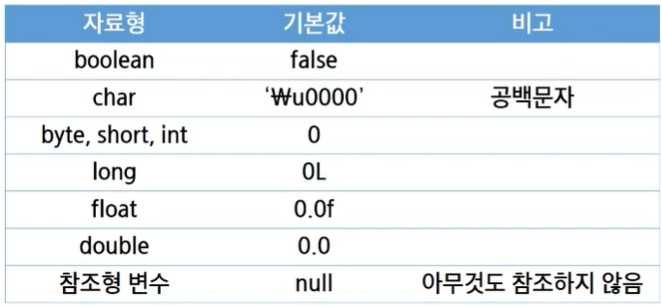
6. Variable and Data type
6.1. Variable
- name of the memory that contains the data
- Rules
- Letters and numbers '$' and '_'
- can't start with numbers
- camelCase
- for variable and functions
- PascalCase: for class
6.2. Data Type (Primitive) <-> (Reference)
-
Primitive Type
-
pre-fixed memory size
-
variable itself has the data
-
types
- Bool
- char(2B)
- byte(1B), short(2B), ==int(4B)==, long(8B)
- float(4B), ==double(8B)==
-
declaration -> assgining
int age; age = 30; int age = 30; // initilazation = declaration + assigning
-
6.3. Type Casting
- byte < short < int < long < float < double
- ==float is bigger than long==
- Implicit Casting
- put smaller data type into bigger data type
- Explicit Casting
- put bigger data type into smaller data type
-
int i = 100; byte b = (byte)i;
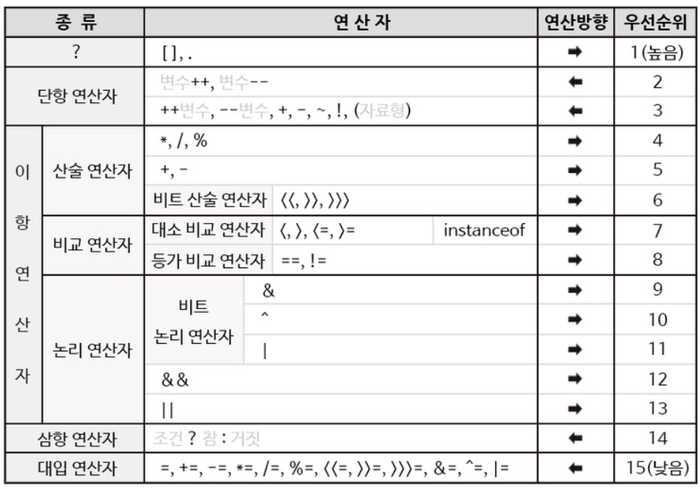
7. Operator
- Equality comparison operator
- ==: compare the value in the variable
- ==not suitable for reference data type==
- equals(): compare the value in the object
- ==suitable for reference data type==
- ==: compare the value in the variable
8. Control flow - condition
8.1. if
public class example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
if(conditional statement) {
statement to run;
}else if(conditional statement2) {
statement to run;
}else {
statement to run;
}
if(conditional statement)
statement to run; // when there's only one statement {}can be skipped
statement to run2; // it isn't included regardless of the index. Not Python!!!
}
}
8.2. switch
public class example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
switch(variable) {
case value1:
statement;
break // break is not mandotry
// but from here all the statements under will be excuted until meet another break
case value2:
statement;
break
default:
statement;
}
}
}
Example.
public class example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int month = 12
switch(month) {
case 1:
case 3:
case 5:
case 7:
case 8:
case 10:
case 12:
System.Out.println("31");
break
case 4:
case 6:
case 9:
case 11:
System.Out.println("30");
case 2:
System.Out.println("28");
break
default:
System.Out.println("Wrong input");
}
}
}
9. Control flow - loop
9.1. if
public class example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (intialization; condition; Incre/Dcre){
statement
}
// intialization, Incre/Decre can be expressed with more than 2 vairables!!
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
System.outl.println(i); // 0 ~ 9
}
for(int i = 0, j = 10; i < 10; i += 2, j--){
System.outl.println(i); // 0, 2, 4, 6, 8
System.outl.println(j); // 10, 9, 8, 7, 6
// multiplication table
for (int i = 2; i <= 9; i++){
for (int j = 2; j <= 9; j++)
System.outl.printf("%d * %d = %d\n", i, j, i * j);
}
}
}
9.2. while
public class example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
while(conditional statement) {
statement;
} // while conditional statement is true
do {
statement;
} while (conditional statement);
// the statement is excuted at least once
}
}
9.3. continue and break
- can be used with ==label=
public class example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
label:
for (int i = 2; i <= 9; i++){
for (int j = 2; j <= 9; j++)
System.outl.printf("%d * %d = %d\n", i, j, i * j);
if (j==3){
continue label;
}
}
}
10. Array
-
Data structure for saving the same type of data
-
==The size is fixed==
-
It's an object == reference data
- The data is saved in heap
- The variable in stack has the address pointing the data
-
String c = "Hi"; String d = "Hi"; String e = new String("Hi"); System.out.println(c == d); //true. There's string pool in heap System.out.println(c == e); //false System.out.println(c.equals(d)); //true
-
can be referenced with index(int)
10.1. Declaration
-
Delacration
- type[] variable
- type variable[]
int[] iArr; char[] cArr; boolean[] bArr; String[] strArr; Date[] dateArr;
-
Creation
-
type[] variable = {v1, v2, v3, }
-
variable = new type[] {v1, v2, v3, }
-
variable = new type[len]
public class array { public static void main(String[] args) { //1-dimensional array int[] score1; int score2[]; score1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; // Impossible score1 = new int[] {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; int[] score2 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} int[] score3 = new int[5]; score3[0] = 1; score3[1] = 2; score3[2] = 3; score3[3] = 4; score3[4] = 5; } }
-
10.2. Usage
-
Arr[index] -
Arr.length -
for-each
-
access to the elements in the array
-
take the elements ==by copying it==
public class foreach{ public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {77, 50, 10, 12, 64, 15} for(int x : arr) { System.out.println(X); // 77, 50, 10, 12, 64, 15 } } }
-
-
Arrays.toString(arr)- change the arr into '[v1, v2, v3, ...]'
-
System.arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length)public class copy{ public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {77, 50, 10, 12, 64, 15} int[] tmp = new int[arr.length*2]; System.arraycopy(arr, 0, tmp, 0, arr.length); //[77, 50, 10, 12, 64, 15, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] } } ```
11. Multidimensional Array
- elements of the array have the address of another array
11.1. Declaration
-
Declaration
- int[][] iArr
- int iArr[][]
- int[] iARr[]
-
Creation
- variable = new type[num_of_1st_array][size_of_1st_array]
- variable = new type[num_of_1st_array][]
int a = 10; int[] arr = new int[4]; //[0, 0, 0, 0] int[][] arr2 = new int[2][]; arr2[0] = new int[3]; arr2[1] = new int[3]; arr2[1][1] = 100; // [[0, 0, 0], [0, 100, 0]]
11.2. Search
- arr[i][j]
- x-search
- arr[i][j+1]: right
- arr[i][j-1]: left
- y-search
- arr[i+1][j]: bottom
- arr[i-1][j]: top
- x-search
다음 포스트