03. Vuex & Lifecycle Hooks
1. Vuex
1.1. Stage Management
What is state?
State is the current data
What is state management?
Sharing the same data state between multiple independent components
1.1.1. Limitations of Pass Props & Emit Events
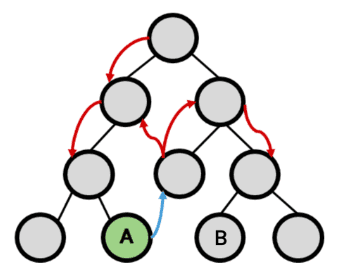
If the depth of the tree is deep, transferring data form to another which is not the parent or a child.
1.1.2. Centralized Store
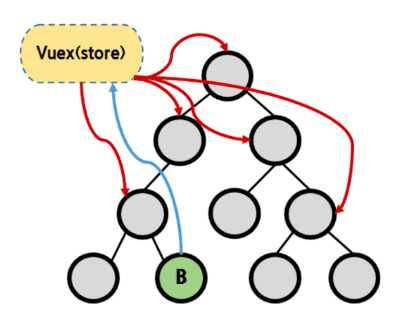
The central storage can be accessed by a node regardless of its depth to obtain or change data. It's preferable for a big or complicated project.
Vuex
Vuex is the central storage of Vue. It also has rules that allow data to change only in predictable ways, therefore it can effectively manage the state.
1.2. Start Vuex
1.2.1. CLI Procedures
vue create {folder_name} // Create a Vue project
cd {folder_name} // Change directory to the created folder
vue add vuex // Apply Vuex to the Vue project
1.2.2. Strcuture of Vuex Instance
If you follow the commands above, src/store/index.js will be newly created. 'index.js' contains a Vuex instance which looks similar to Vue instance.
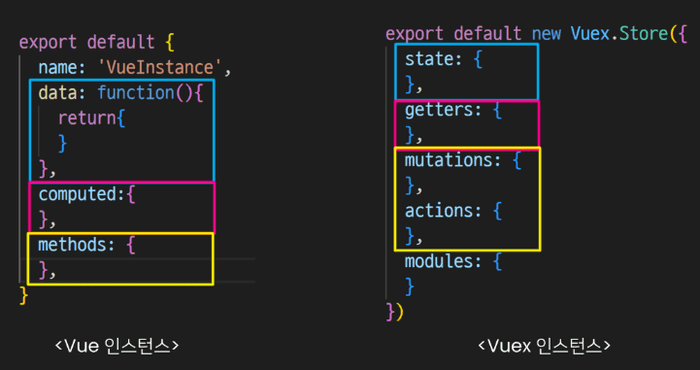
- state
- corresponds to the data in the Vue instance.
- There's dat which is manged in the centralized storage.
- It can be accessed from othe components by
vueInstance.$store.state
- getters
- corresponds to the computed in the Vue instance.
- It also chaches the processed data.
- All the functions in the mutations get
state,getteras the first two arguments.
- mutations
- corresponds to the methods in the Vue instance, and it only 0can change the state.
- To specify the moment when the state is changed, all the functions in the mutations should be synchronous.
- All the functions in the mutations get
stateas the first argument. - It can be called through
vuexInstance.commit()method.
- actions
- corresponds to the methods in the Vue instance, and it should not change the state.
- A function in the actions can contain asynchronous process. If it calls a function in the mutations to change the state.
- All the functions in the actions get
contextas the first argument. It can be called throughvuexInstance.dispatch()method.
1.2.3. Data Flow through Vuex
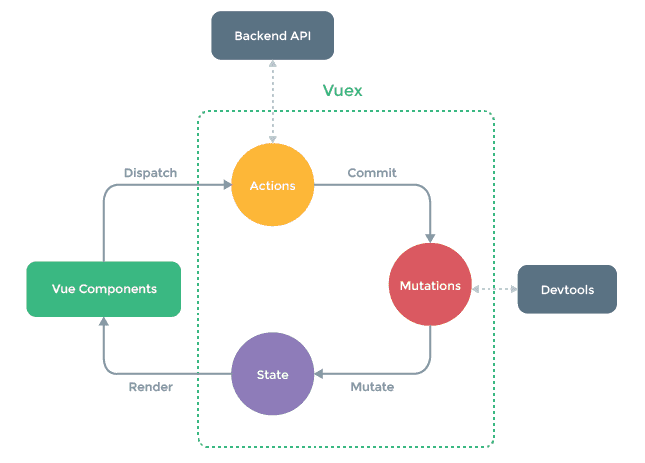
-
Manipulating the state
- component -> (actions) -> mutations -> state
-
Using the state
- state -> (getters) -> component
1.3. Practice Vuex
index.js
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
message: 'message in store',
},
getters: {
messageLength(state) {
return state.message.length
},
},
mutations: {
CHANGE_MESSAGE(state, message) {
state.message = message
},
},
actions: {
changeMessage(context, message) {
context.commit('CHANGE_MESSAGE', message)
},
},
modules: {},
})
App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>{{ message }}</h1>
<h3>message length: {{ messageLength }}</h3>
<input type="text" @keyup.enter="changeMessage" v-model="inputData" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
data() {
return {
inputData: null,
}
},
computed: {
message() {
return this.$store.state.message
},
messageLength() {
return this.$store.getters.messageLength
},
},
methods: {
changeMessage() {
const newMessage = this.inputData
this.$store.dispatch('changeMessage', newMessage)
this.inputData = null
},
},
}
</script>
2. Lifecycle Hooks
2.1. Lifecycle Hooks
There are several points which can be specified in the lifecyle of a Vue instance. It's possible to automatically execute a preset logic at each point.
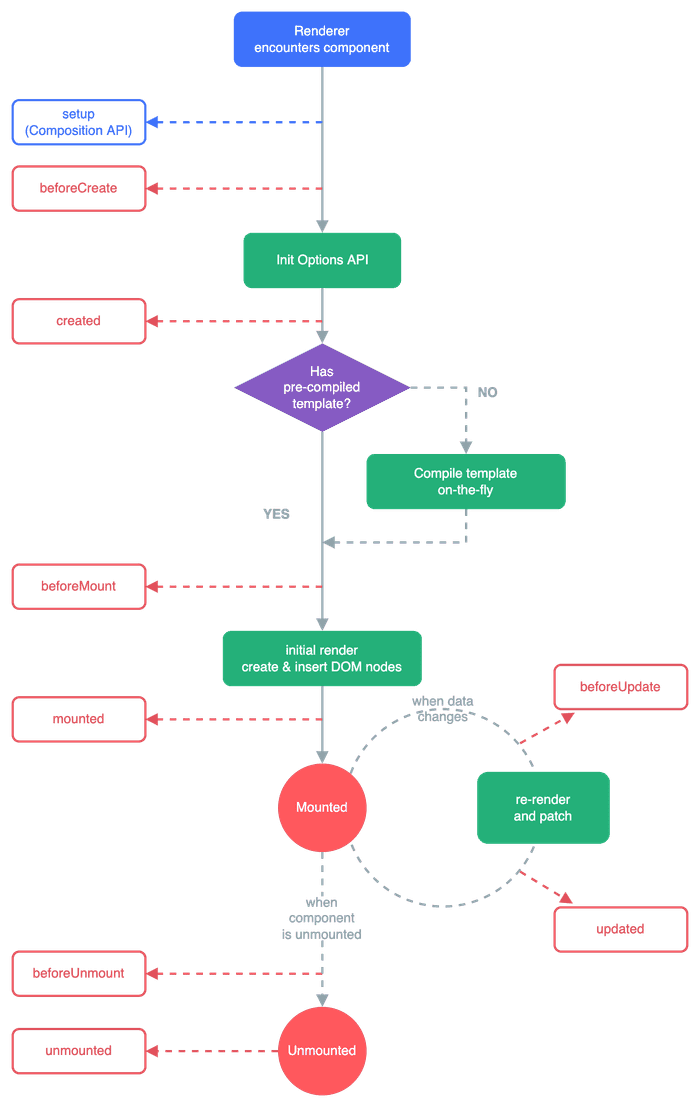
-
create
The point when the Vue instance is created -
mount
The point when the Vue instance is linked to the DOM -
update
The point when the DOM is updated -
destroy
The point when the Vue instance is destroyed
Example code
export default {
...
beforeCreate() {
console.log('beforeCreate')
},
created() {
console.log('created')
},
beforeMount() {
console.log('beforeMount')
},
mounted() {
console.log('mounted')
},
}
3. Todo List CRUD Practice with Vuex
3.1. Local Storage
Local Stoarge and Session Storage
A browser storage where data is saved in key-value form. The key is used for distinguising the data source, and the value is sotred as JSON string. This sotorage is maintained until it is intentionally deleted.
- F12 -> Application -> Storage -> Local Storage
3.1.1. Window.localStorage
The object which has mehtods for manipulating local sotrage.
localStorage.setItem(key: string, value: string)
Store the value in the local storage with the key.
To change JS object into JSON, you can use JSON.stringfy()
localStorage.getItem(key: string)
Get the value of the key from the local storage.
To change JSON into JS object, you can use JSON.parse()
3.1.2. vuex-persistedstate
The library which has function for automatically storing and reloading Vuex state.
Install
npm i vuex-persistedstate
Apply
// index.js
import createPersistedState from 'vuex-persistedstate'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.STore({
plugins: [createPersistedState()],
})
3.2. Code
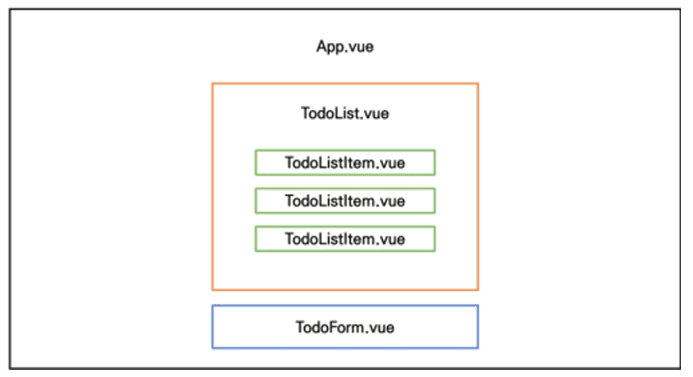
3.2.1. index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import createPersistedState from 'vuex-persistedstate'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
plugins: [createPersistedState()],
state: {
todos: [],
},
getters: {
allTodosCount(state) {
return state.todos.length
},
// The number of completed todoItems
completedTodosCount(state) {
const completedTodos = state.todos.filter((todo) => {
return todo.isCompleted === true
})
return completedTodos.length
},
// The number of uncompleted todoItems
unCompletedTodosCount(state, getters) {
return getters.allTodosCount - getters.completedTodosCount
},
},
mutations: {
CREATE_TODO(state, todoItem) {
state.todos.push(todoItem)
},
DELETE_TODO(state, todoItem) {
const index = state.todos.indexOf(todoItem)
state.todos.splice(index, 1)
},
// Change isCompleted attribute of todoItem
UPDATE_TODO_STATUS(state, todoItem) {
console.log(todoItem)
state.todos = state.todos.map((todo) => {
if (todo === todoItem) {
todo.isCompleted = !todo.isCompleted
}
return todo
})
},
// // createPersistedState() replaced this function.
// LOAD_TODOS(state) {
// const localStorageTodos = localStorage.getItem('todos')
// const parsedTodos = JSON.parse(localStorageTodos)
// state.todos = parsedTodos
// },
},
actions: {
createTodo(context, todoTitle) {
const todoItem = {
title: todoTitle,
isCompleted: false,
}
context.commit('CREATE_TODO', todoItem)
// context.dispatch('saveTodosToLocalStorage')
},
deleteTodo(context, todoItem) {
context.commit('DELETE_TODO', todoItem)
// context.dispatch('saveTodosToLocalStorage')
},
updateTodoStatus(context, todoItem) {
context.commit('UPDATE_TODO_STATUS', todoItem)
// context.dispatch('saveTodosToLocalStorage')
},
// // createPersistedState() replaced this function.
// saveTodosToLocalStorage(context) {
// const jsonTodos = JSON.stringify(context.state.todos)
// localStorage.setItem('todos', jsonTodos)
// },
// // createPersistedState() replaced this function.
// loadTodos(context) {
// context.commit('LOAD_TODOS')
// }
},
modules: {},
})
3.2.2. App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>Todo List</h1>
<h2>Number of All Todos: {{ allTodosCount }}</h2>
<h2>Number of Completed Todos: {{ completedTodosCount }}</h2>
<h2>Number of Uncompleted Todos: {{ unCompletedTodosCount }}</h2>
<TodoList />
<TodoForm />
<!-- <button @click="loadTodos">Reload Todo List</button> -->
</div>
</template>
<script>
import TodoList from '@/components/TodoList'
import TodoForm from '@/components/TodoForm'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
TodoList,
TodoForm,
},
computed: {
allTodosCount() {
return this.$store.getters.allTodosCount
},
completedTodosCount() {
return this.$store.getters.completedTodosCount
},
unCompletedTodosCount() {
return this.$store.getters.unCompletedTodosCount
},
},
methods: {
loadTodos() {
this.$store.dispatch('loadTodos')
},
},
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
</style>
3.2.3. TodoForm.vue
<template>
<div>
<input type="text" v-model.trim="todoTitle" @keyup.enter="createTodo" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'TodoForm',
data() {
return {
todoTitle: null,
}
},
methods: {
createTodo() {
if (this.todoTitle) {
this.$store.dispatch('createTodo', this.todoTitle)
}
this.todoTitle = null
},
},
}
</script>
3.2.3. TodoList.vue
<template>
<div>
<TodoListItem v-for="(todo, index) in todos" :key="index" :todo="todo" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
import TodoListItem from '@/components/TodoListItem'
export default {
name: 'TodoList',
components: {
TodoListItem,
},
computed: {
todos() {
return this.$store.state.todos
},
},
}
</script>
<style></style>
3.2.3. TodoListItem.vue
<template>
<div>
<span
@click="updateTodoStatus"
:class="{ 'is-completed': todo.isCompleted }">
{{ todo.title }}
</span>
<button @click="deleteTodo">Delete</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'TodoListItem',
props: {
todo: Object,
},
methods: {
deleteTodo() {
this.$store.dispatch('deleteTodo', this.todo)
// this.$store.commit('DELETE_TODO', this.todo)
},
updateTodoStatus() {
this.$store.dispatch('updateTodoStatus', this.todo)
},
},
}
</script>
<style>
.is-completed {
text-decoration: line-through;
}
</style>