SQL Basics
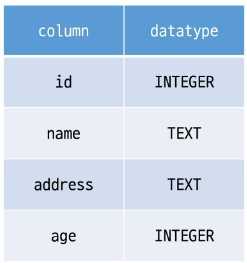
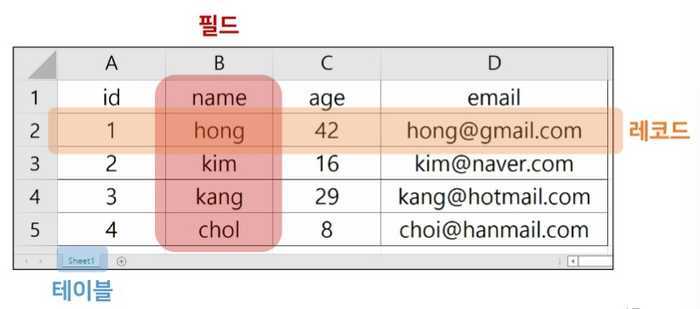
1. Database
organized collection of data
1.1. RDB
- RDB(Relational Database)
- Managing data by dividing it into multiple tables
- A table can reference another table with its' primary key
- RDBMS(Relational Database Management System)
- Program for managing RDB
- Ex. SQLite, MySQL, Oracle, ...
1.2. Structure
- Schema
- Table
2. SQL
2.1. SQL
Structured Query Language, the programming language for managing dabtabase in RDBMS
2.2. Types of SQL Commands
| Type | Concept | SQL keywords |
|---|---|---|
| DDL (Data Definition Language) |
CUD of a table | CREATE DROP ALTER |
| DML (Data Manipulation Language) |
CRUD of records | INSERT SELECT UPDAE DELETE |
| DCL (Data Control Language) |
security, restriction, authorization | GRANT REVOKE COMMIT ROLLBACK |
2.3. SQL Syntax
- Statement
- A complete code that can be excuted
- Ends with ';'
- Clause
- Subunit of statement
SELECT column_name FROM table_name;- One SELECT statement
- Two clauses
SELECT column_nameFROM table_name
2.4. Import .csv to Table
- Create a table
sqlite3 mydb.sqlite3.mode csv.import file_name table_name
3. DDL
Data definition language deals with table
3.1. CREATE TABLE
CREATE TABLE table_name (
column_1 data_type constraints,
column_2 data_type constraints,
column_3 data_type constraints
);
- Data Types
-
Constraints
- NOT NULL
- NULL is not allowed
- UNIQUE
- Should be unique from other records' values.
- PRIMARY KEY
- Column identifying the record
- Availabe for only INTEGER type columns
- Even if the pk column is not designated, the pk column exists under the name 'rowid'.
- AUTOINCREMENT
- By default, the starting value for AUTOINCREMENT column is 1, and it will increment by 1 for each new record.
- NOT NULL
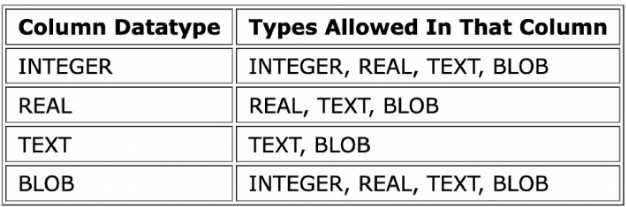
3.1.1. Datatypes In sqlite3
-
Data Type
- NULL
- INTEGER
- REAL
- float
- TEXT
- BLOB
- Binary Large Object
-
Dynamic Type System
- Even if you do not specify the data type for the column, the data type is determined according to the data saved
- Therefore, about the same column, if 1 is put, it becomes an integer, and if '1'is put, it becomes a string
- But for compatibility with other RDBMS, It's strongly recommend to announce the datatype.
-
Static, Rigid Typing
-
Type Affinity
3.2. ALTER TABLE
ALTER TABLE table_name RENAME TO new_table_name;
ALTER TABLE table_name RENAME COLUMN column_name TO new_column_name;
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD COLUMN column_name data_type constraints DEFAULT defalut_value;
ALTER TABLE table_name DROP COLUMN column_name;
-- Dropping column is impossible when,
-- Foreign Key
-- Primary Key
-- UNIQUE
3.3. DROP TABLE
DROP TABLE table_name
4. DML
Data manipulation language deals with records
4.1. SELECT
-
SELECT
SELECT * FROM table_name; SELECT rowid, column1, column2 FROM table_name; SELECT DISTINCT column1, column2 FROM table_name; --- after eliminating duplicated data --- {colun1, column2} is one element of the set -
ORDER BY
SELECT column_list FROM table_name ORDER BY column1 ASC, column2 DESC; --- order data by column1 first --- and then order by column2, if the data of column1 is the same --- NULL is treated as the smallest value -
WHERE
SELECT column_list FROM tbale_name WHERE search_condition; ---search_condition WHERE column1 = 10 WHERE column1 > 10 AND column2 <= 200 WHERE column2 LIKE 'Ko%' WHERE column3 IN (1, 2) WHERE column4 BETWEEN 10 AND 20- Comparision Operators
- =, !=
- >, <, >=, <=
- Logical Operators
- AND, OR, NOT
- LIKE operator
- Not case-sensitive
- %: 0 or more arbitrary characters
- _: one arbitrary characger
- IN operator
- whether the value is in the list
WHERE column3 IN (1, 2) WHERE column3 = 1 OR column3 = 2 - BETWEEN operator
- whether the value is in the range
WHERE column4 BETWEEN 10 AND 20 WHERE column4 >= 10 AND column4 <= 20
- Comparision Operators
-
LIMIT
SELECT column_list FROM tbale_name LIMIT row_count; SELECT column_list FROM tbale_name LIMIT row_count OFFSET offset_count; SELECT column_list FROM table_name ORDER BY column1 ASC LIMIT row_count;- OFFSET keyword
LIMIT 10 OFFSET 10 --- 11 ~ 20
- OFFSET keyword
-
GROUP BY
SELECT aggregate_function(column1) FROM table_name WHERE search_condition; SELECT column1 FROM table_name GROUP BY column2; -- usually column1 group by column1 SELECT column1, aggregate_function(column2) FROM table_name GROUP BY column3;- Aggregate function
Datatype should be INTEGER except COUNT()- AVG()
- COUNT()
- MAX()
- MIN()
- SUM()
- Aggregate function
-
Order of Queries
SELECT ___ FROM ___ WHERE ___ GROUP BY ___ ORDER BY ___ LIMIT ___
4.2. INSERT
INSERT INTO table_name (column_list) VALUES (value_list);
INSERT INTO table_name VALUES (value_list);
--- when column_list is omitted, you should put all the values in order
INSERT INTO table_name VALUES
(value_list1),
(value_list2),
(value_list3),
(value_list4);
4.3. UPDATE
UPDATE table_name
SET column1 = value1, column2 = vlaue2
WHERE search_conditon;
4.4. DELETE
DELETE FROM table_name
WHERE search_conditon;
--- when the WHERE caluse is omitted, all the data is deleted
이전 포스트
Django QuerySet
다음 포스트